What is Decentralized finance (DeFi)?
Decentralized finance (DeFi) refers to financial systems based on DLT that, unlike classic financial systems, do not require the participation of intermediaries such as banks or exchanges.
By using smart contracts and decentralized protocols (dApps), DeFi systems facilitate peer-to-peer transactions for financial operations. Unlike other many financial services, DeFi requires no user identification.
Advantages of DeFi in Banking
Advantages of DeFi in banking include fast transaction processing and opportunities to generate income from cryptocurrencies.
DeFi lending vs. DeFi staking
Two of the most important uses of DeFi are:
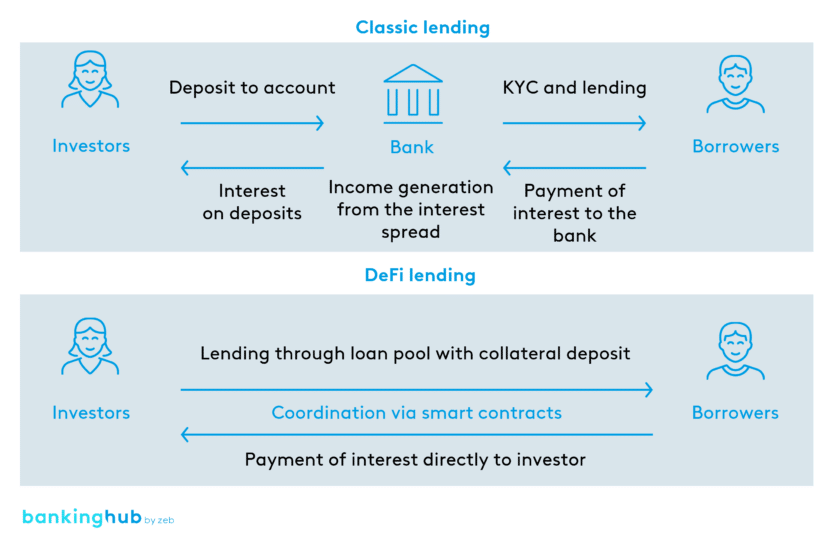
DeFi lending
Lending protocols enable peer-to-peer lending, where participants grant each other loans without involving banks as intermediaries. For this purpose, lenders deposit cryptocurrencies into so-called lending pools.
To obtain loans from a lending pool, borrowers simply need to deposit cryptocurrencies as collateral. Due to the collateral deposited, a credit check is generally not required.
DeFi staking
Users support the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism of a DLT system with their cryptocurrencies. They lock a portion of their cryptocurrencies in their wallet using staking protocols, allowing them to act as validators of transactions on the DLT system.
To incentivize users to participate in staking, the DLT protocol rewards them with tokens of the respective DLT system’s native cryptocurrency.