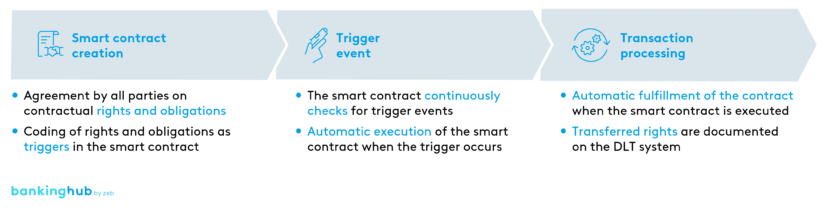
How does a smart contract work?
A smart contract is a program that digitally represents the terms of a contract between two or more parties on a DLT system. When one party fulfills its obligations as defined in the contract, the smart contract automatically fulfills the obligations of the other party. This may include, for example, the transfer of ownership of a security upon receipt of a payment.
What are the advantages of smart contracts?
The advantages of smart contracts include secure, fast, and prospectively cost-effective transaction processing.
- By automatically executing transactions, Smart Contracts ensure compliance with the terms of the contract, providing security and thereby building trust. This is reinforced by the fact that all transactions are stored transparently and tamper-proof on the respective DLT system and the program code of a smart contract is publicly visible.
- Due to the immediate and automated execution, transactions can be processed in near real time. In addition, cost savings can be achieved as fewer intermediaries are required compared to traditional transactions.
Use cases for smart contracts
- Use cases for smart contracts may include the tokenization of assets or the creation of non-fungible tokens.
- Furthermore, smart contracts can be used to greatly support the digitalization of international trade by representing purchase agreements in the supply chain.
- In addition, the use of smart contracts in post-trading can significantly speed up the settlement of securities.