How does a wallet work?
A crypto wallet (or wallet for short) is a physical device or software that generates, secures, and stores public and private keys. Users can send and receive tokens and view their account balance via the wallet.
However, the tokens themselves are stored on the blockchain and not in the wallet, which can only be used for custody of the private and public keys. Therefore, in token transactions, it is not the tokens that are transferred between the wallets of the parties involved, but rather the corresponding access rights to those tokens.
Public-key cryptography
In public-key cryptography, an algorithm generates a mathematically linked key pair consisting of a private key and a public key.
- The private key must be kept secret by the respective user.
- The public key, on the other hand, is known to all members of the blockchain network and is used to identify the individual user.
Using the private key, a user can digitally “sign” any dataset and send it to a recipient in the blockchain network. The recipient can then verify the authenticity of the dataset by using the sender’s public key (provided the two keys correspond).
Keys play a crucial role in establishing trust with regard to DLT systems.
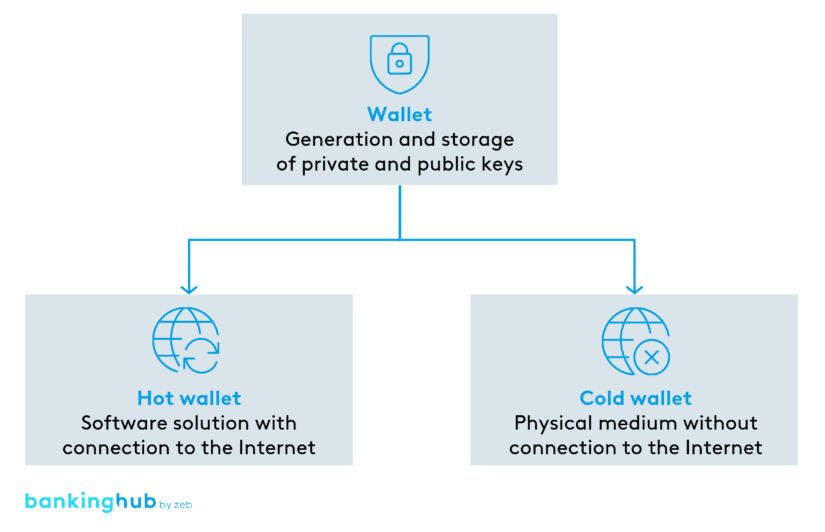
Hot wallets vs. cold wallets?
Wallets are divided into hot wallets and cold wallets. Hot wallets are software solutions that are connected to the Internet. In contrast, cold wallets are hardware solutions that store keys offline using physical media that are not connected to the Internet.
While cold wallets are resistant to cyberattacks and therefore highly secure, hot wallets are the more common type of wallet due to their ease of use.