What is the difference between cryptocurrencies and crypto assets?
Cryptocurrencies are fungible digital assets secured by cryptographic encryption to prevent forgery and tampering during transactions. They are intended to act as virtual alternatives to classic fiat currencies and enable users to make digital payments for goods and services independently from centralized institutions.
Cryptocurrencies are crypto assets that are not issued or guaranteed by any public authority and do not have the legal status of currency or money. Nevertheless, cryptocurrencies are accepted as a medium of exchange, payment, or investment. Crypto assets as a superordinate category are regulated on a pan-European level under Art. 3 (1) no. 2 of the Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCAR).
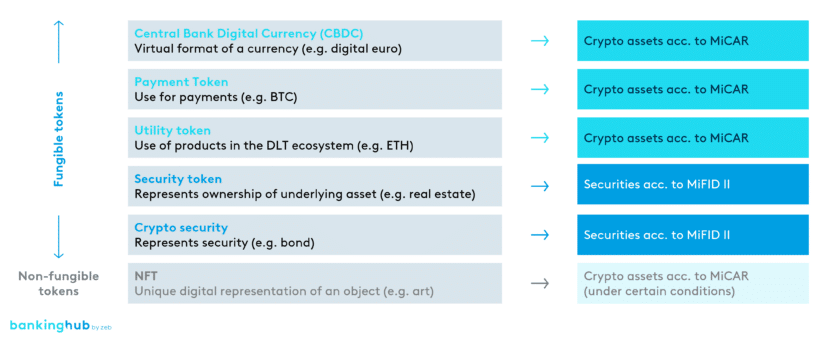
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), payment tokens and utility tokens
Cryptocurrencies can further be subdivided into Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), payment tokens and utility tokens. In Europe, all of these categories are subject to the MiCAR.
- CBDCs are tokens of a fiat currency designed to be stable in value.
- Payment tokens are digital assets that are used exclusively for payments in various environments (i.e. they aren’t limited to, say, a specific platform). Examples of payment tokens include Bitcoin as well as stablecoins like Tether.
- Utility tokens, by contrast, grant certain access rights within a predefined environment (e.g. access to digital services or products). Their purpose is non-financial in nature and concerns the operation of digital platforms or services.