|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Introduction of open banking

Open banking can become one of the main driving forces of innovation in financial and capital markets.
Can you briefly explain the concept and implications of open banking?
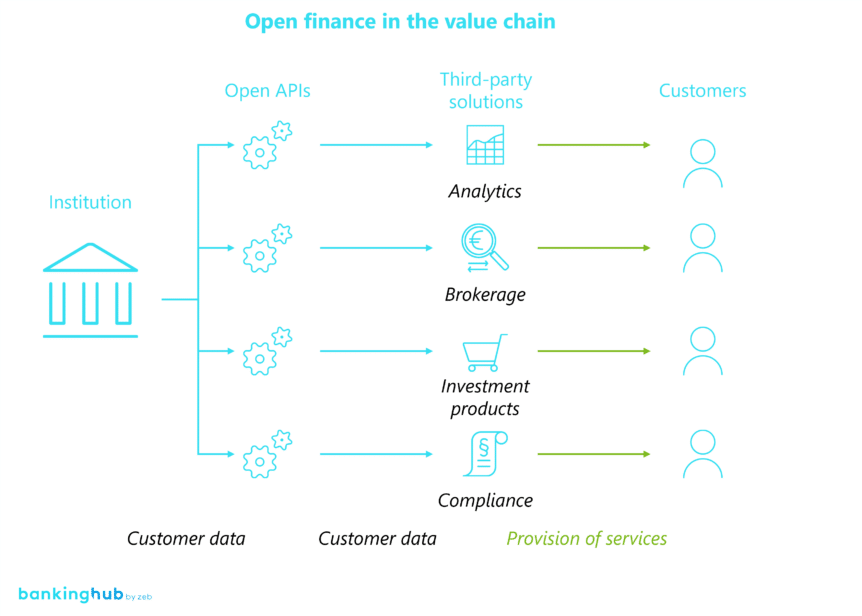
Open banking is a concept that enables consenting bank customers to share their financial data and services with authorized third-party providers. This allows the closed financial world to evolve into an open, customer-centric ecosystem that interconnects customers, banks, and other providers such as fintech companies.
Open banking is based on regulatory frameworks such as the EU’s Payment Services Directive (PSD2), which gives authorized third parties access to account information and payment services.
This concept is critical to the future of the financial sector because it enables new business models and partnerships, thereby creating new opportunities for customers and providers. It is helping to transform processes and create a more interconnected financial ecosystem. By leveraging APIs, platforms and the cloud, banks are providing their customers with data-based solutions that improve real-time access to data and streamline decision-making processes.
We at zeb also see great potential in the use of open banking and are observing the first use cases. How do you think open banking can change traditional banking practices?
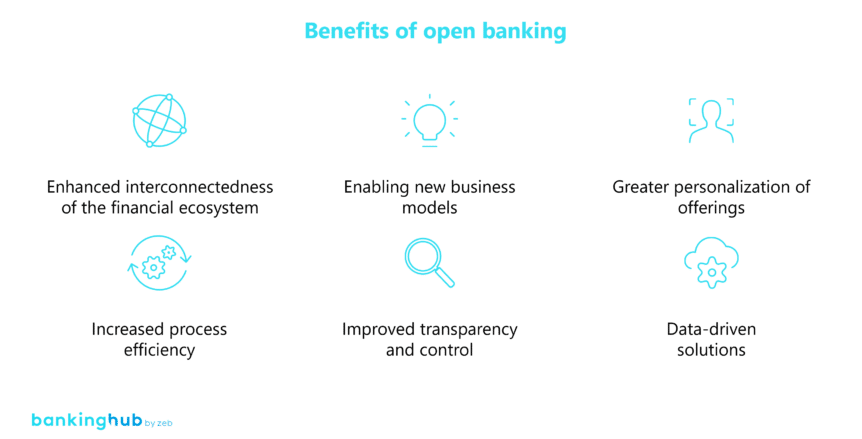
Open banking can transform traditional banking practices by providing customers with more choice, transparency and control of their financial data and services. By opening up interfaces for third-party providers, customers can benefit from innovative and personalized offerings. Open banking enables banks to increase their competitiveness and efficiency by developing new business models, partnerships, and platforms.
However, open banking also poses challenges for traditional banks, such as protecting customer data, complying with regulatory requirements, adapting organizational structures, and coping with increased competitive pressure.
BankingHub-Newsletter
Analyses, articles and interviews about trends & innovation in banking delivered right to your inbox every 2-3 weeks
"(Required)" indicates required fields
Development and outlook
According to our research, open banking is almost a decade old. Have the benefits promised by the open banking initiatives materialized yet?
Open banking is indeed almost a decade old, but it has gained momentum in recent years – particularly in Europe, where the aforementioned PSD2 directive has laid down the legal framework for data exchange between banks and third-party providers. One of the benefits of open banking that has already emerged is greater choice for the customers of financial services providers, as they are able to share their financial data with their preferred third-party providers. There is also more competition and innovation in the financial sector through new business models that offer customers better and more personalized products. Another benefit is that open banking enables more efficient and faster payments, with lower costs and real-time processing.
However, there are challenges that prevent the full benefits of open banking from being realized. These include a lack of customer acceptance, as many customers are not yet aware of the benefits of open banking or have concerns about security and data protection issues. Inconsistent regulatory standards and technical specifications are also hampering the interoperability and scalability of open banking solutions. Traditional banks are still experiencing resistance and adaptation difficulties as they need to change their existing business models, organizational structures, and IT systems to keep pace with the new requirements.
What are the current trends in open banking?
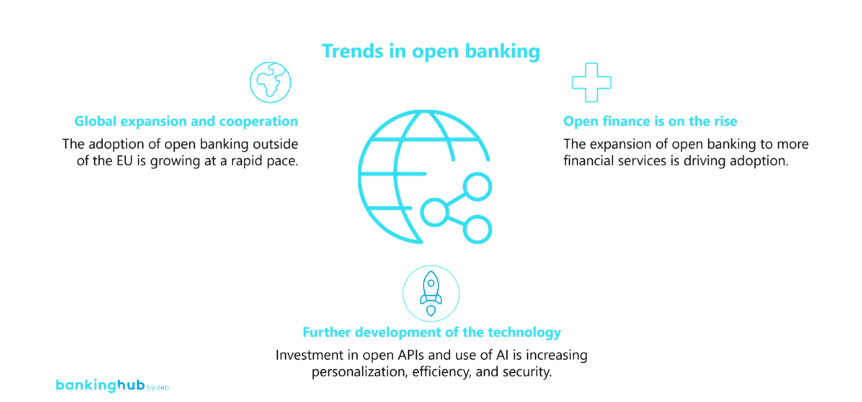
It is remarkable how fast open banking is currently spreading. Both banks and fintech companies are increasingly recognizing the benefits of collaboration in the open banking ecosystem. Banks benefit from the agility and innovative strength of fintech companies, while fintech companies in turn benefit from the reach and expertise of banks. As a result, the use of open banking is now increasingly spreading beyond Europe to other regions of the world. Approaches and levels of maturity vary depending on the degree to which banks, fintech companies, and regulators are active in the respective regions.
In addition, open finance, as an extension of open banking to other financial areas such as insurance, investments, and retirement planning, is gaining traction. It enables customers to obtain a comprehensive overview of their financial situation and recommendations for optimal solutions that match their specific needs. The importance of open finance continues to grow, as found by a Finastra survey of German companies conducted in 2023. More than 90% of the companies surveyed stated that open finance is a must-have or at least an important topic. This development is in line with increased investment in open APIs, with a quarter of institutions planning to develop or deploy this technology within the next 12 months – an increase compared to 18% in the previous year.
Open banking solutions are also becoming more sophisticated. The use of artificial intelligence (AI), for example, is playing a decisive role in this context. AI is enabling providers to offer more personalized products and is helping to increase the efficiency and security of open banking solutions. In addition, advances in encryption, authentication, and consent solutions are helping to improve the security of customer data, thereby increasing adoption.
Use cases from the capital market
How can open banking and open finance contribute to the further development of business models and create new opportunities, particularly in capital markets?
Through various approaches, open banking and open finance can support the further development of business models and the creation of new opportunities in the capital markets, including the integration of banking and non-banking services. This primarily involves the combination of payment, lending, insurance, and investment products to meet individual customer needs.
In addition, open banking and open finance promote the establishment of platforms and ecosystems that connect different financial players. These ecosystems provide added value for all stakeholders, for example by connecting brokers, exchanges, asset managers, regulators, and customers. This fosters not only cooperation but also innovation in the financial sector.
Another important aspect is to promote the use of data and artificial intelligence. Open banking and open finance make it possible to harness large amounts of data and analyze it with AI technologies. This leads to improvements in several areas, such as optimizing risk, pricing, and portfolio strategies, identifying market opportunities and trends, and tailoring products and services to individual customer profiles. Open banking and open finance therefore play a crucial role in transforming and adapting business models in the financial sector.
How can open banking and open finance use cases be integrated into the capital markets’ value chain? What are specific use cases?
These are some use cases for the effective integration of open finance into the capital markets value chain:
Starting with risk management, open finance can provide more detailed and up-to-date data on exposures, counterparties, and market conditions. This leads to greater accuracy and reliability of risk models, stress testing and scenario analyses, and supports compliance with regulatory requirements such as Basel III and MiFID II.
For liquidity management, open finance can help financial institutions to optimize their liquidity and cash flow. This is done by accessing real-time data from multiple bank accounts and payment service providers. Such an approach enables faster and cheaper cross-border payments, improved forecasting and hedging, and a more efficient allocation of capital and financial resources.
Lastly but not least, open finance can also increase customer satisfaction for capital market companies. By offering customized products and services, open finance can help increase customer loyalty and retention, as well as reach new segments and markets. This offering includes, for example, dynamic pricing, individual advice and automated execution.
Finastra’s open banking solutions
Can you give an overview of Finastra’s solutions related to open banking and open finance and describe the key features and challenges in a concrete example?
Finastra offers a range of solutions that enable and support open banking as they are based on an open architecture that accelerates collaboration and innovation in the financial industry. A prominent example of such an open banking solution is our “FusionFabric.cloud” platform. This platform is characterized by its openness, making it possible to create and use APIs that cover various areas such as risk management, collateral management, and reporting. The platform is also based on a secure and reliable cloud infrastructure, which guarantees high availability and flexibility. This in turn ensures scalability. FusionFabric.cloud serves as a common marketplace for APIs, thus facilitating collaboration among the various financial players.
This solution addresses several challenges in the financial services industry. It accelerates innovation by providing access to new technologies, partners, and markets, which in turn generates new business models and products. Possible solutions include retail and corporate banking, payments, lending, treasury, and capital markets. It also improves customer loyalty and satisfaction by providing customers with greater transparency of their financial data and recommending optimized solutions. The app economy, which enables new business models and customer offerings, brings together the best innovations from the financial sector and facilitates collaboration and the exchange of ideas and technologies. Lastly, FusionFabric.cloud increases process efficiency and security by reducing the effort and error rates associated with traditional IT systems and interfaces.
In summary, with FusionFabric.cloud, Finastra aims to transform the way modern banking software is developed, provided and used to support the new era of innovation and collaboration in the financial sector.