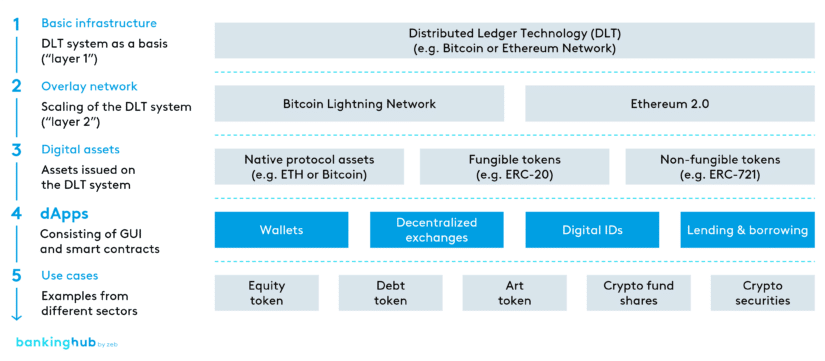
How do dApps work?
A decentralized application (dApp) is a software application that runs on a DLT system. dApps comprise a smart contract that functions as the back end, and a graphical user interface (GUI) that acts as the front-end.
By combining smart contracts with a GUI, dApps make numerous functions of DLT systems accessible to end users.
dApps vs. other software applications
A key difference from other software applications is that the back end of dApps runs on a decentralized DLT system instead of a central server.
Therefore, the transactions performed by a dApp are also verified by the DLT network. As a result, dApp users benefit from the advantages of DLT such as security and transparency.
Use cases for dApps in the financial industry
By automatically executing underlying smart contracts upon the occurrence of specific conditions, dApps facilitate trust and enable numerous use cases for peer-to-peer transactions.
Since dApps are based on smart contracts, they typically run on Ethereum Virtual Machine-compatible blockchains such as Ethereum, Solana, or Polygon.
Use cases in the financial industry include, for example, the creation of security tokens or the issuance of crypto securities. In addition, dApps can be used to create non-fungible tokens. Numerous applications in decentralized finance also use dApps.