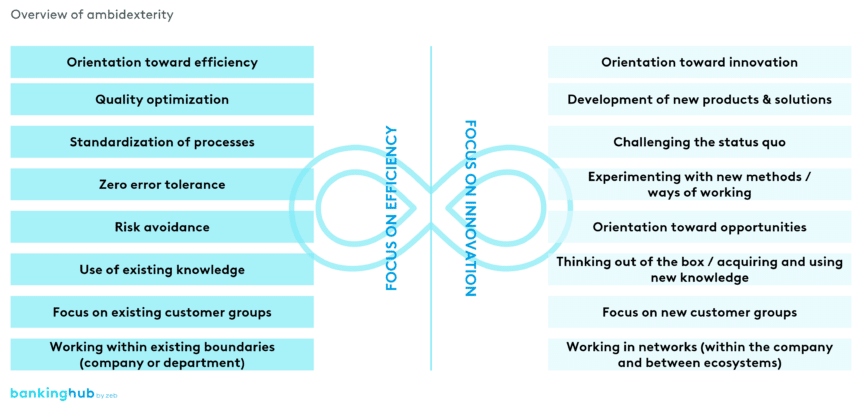
Key aspects of ambidexterity
By embracing ambidexterity, companies can optimize their existing business processes while concurrently developing new, forward-looking ones.
- optimizing and enhancing the efficiency of existing processes, products and services.
- seeking and implementing new ideas, innovations and technologies.
The relevance of ambidexterity in today’s banking and insurance world
In today’s dynamic financial landscape, ambidexterity – the organization’s ability to be both efficient and innovative at the same time – is paramount for banks and insurance companies. The advancement of digitalization, coupled with evolving regulatory requirements and mounting pressure from fintech and insurtech companies, compels established financial institutions to simultaneously optimize their traditional business models and develop new, forward-looking approaches.
Within the banking sector, this means maintaining efficient and reliable processes in traditional banking operations such as lending and risk management while concurrently developing and implementing new, innovative digital business models and technologies.
… and this relevance continues to grow
- Technological innovation: New technologies, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain and big data, are fundamentally reshaping the financial landscape. Financial institutions must strike a balance between maintaining the efficiency of their traditional systems and strategically investing in these emerging technologies.
- Changing customer demands: Customers increasingly demand digital, rapid and personalized services. Ambidexterity allows financial institutions to enhance existing services while simultaneously developing innovative offerings.
- Regulatory requirements: The financial industry operates within a highly regulated environment. Ambidexterity enables institutions to efficiently meet existing compliance requirements while remaining adaptable to new regulatory changes.
- Competitive pressure: Intense competition from fintech and insurtech companies is forcing traditional banks and insurers to constantly innovate to remain competitive.
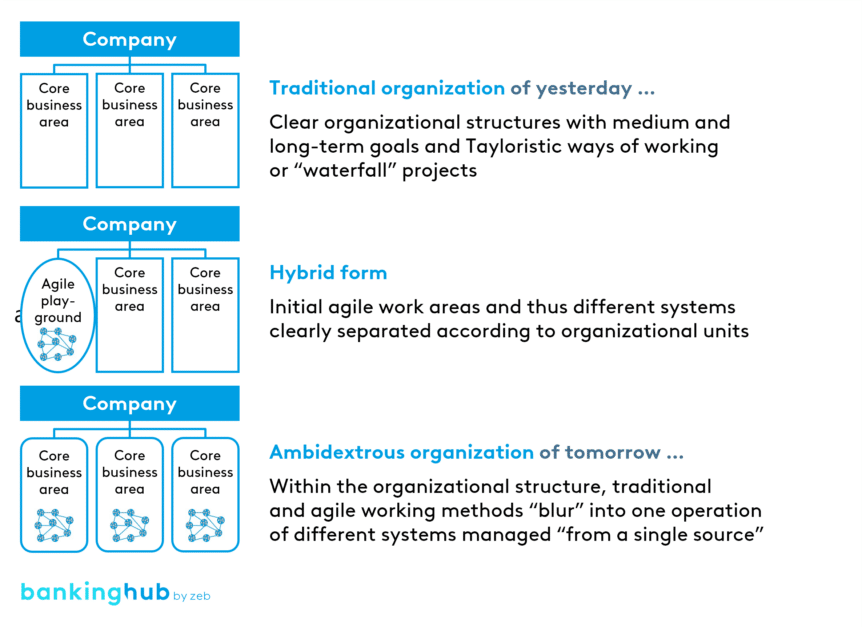
Strategic facets of ambidexterity
Implementing ambidexterity in banks and insurance companies requires thoughtful strategic planning and execution. It is not only an operational challenge. It is a strategic necessity.
- Dual business models: Companies need to invest in their traditional business models while also developing new, innovative business areas. This requires a clear separation of the two approaches, but also their integration.
- Flexible leadership: Ambidexterity demands a new type of leadership – one that fosters stability in processes while encouraging creative innovation. Executives need to be flexible and adaptable to effectively manage both realms.
- Resource management: Resources must be allocated in a binding manner in order to support the efficiency of existing processes and core business while also nurturing new ideas. This may involve creating dedicated budgets for innovation.
- Cultural change: The corporate culture must evolve to foster openness to change and a willingness to innovate. Targeted change management programs can facilitate this cultural shift.
Barriers to implementing ambidexterity
The implementation of ambidexterity in banks and insurance companies is associated with considerable challenges. These can be both structural and cultural.
- Organizational inertia: Traditional banks and insurance companies often operate within rigid structures and processes, hindering change and adaptability.
- Cultural barriers: A risk-averse culture that prioritizes stability may impede innovation and flexibility.
- Resource conflicts: Allocating resources between existing and new business areas may lead to internal conflicts.
- Management complexity: Effectively managing efficiency-oriented and innovation-driven activities simultaneously demands specialized management skills and leadership approaches.
Checklist: Recommendations for implementation in practice
Successful implementation of ambidexterity in banks and insurance companies requires strategic and operational measures. The following are recommended for implementation:
Establish dual structures
Separate the units for traditional business and innovation to create an environment conducive to both areas. Cultivate specific cultural characteristics within each unit. For instance, maintain a zero error tolerance in efficiency areas and foster an open culture and the courage to make mistakes in innovation areas. Different incentives and objectives support this dual structure.
At the same time, executives with an eye out for efficiency and innovation are needed, regardless of the unit in which they work. This is because a complete separation ultimately leads to silo thinking rather than a dual, synchronized system.
Clear objectives are crucial for formulating expectations related to products, processes and other aspects. The path to achieving these objectives should also be described, whether it involves an expected level of detail, control loops, high implementation speed, or the development of new, innovative products with a pilot character. By adopting this approach, both perspectives can be integrated at a higher level. A leaning toward either efficiency or innovation can streamline work processes and provide clearer guidance for teams and employees.
Encourage flexible leadership
Training and development programs for executives should aim to support both efficiency and innovation, providing the ability to recognize when either creativity-promoting leadership or tighter control is required. However, both approaches should be part of executives’ toolbox.
Utilize breathing target systems and HR tools
Strategic and operational goals require vigilant monitoring and timely adjustments. This principle applies equally to efficiency and innovation areas. By adapting to dynamic changes during the year, new targets can be set at short notice.
Furthermore, strategies should undergo frequent review and adjustment in short cycles. In today’s dynamic landscape, it is not uncommon for new trends to emerge in the short term, prompting a reprioritization of topics and projects within long-term planning.
Implement incubation programs
Establish innovation centers or incubators to develop and test new ideas in a controlled environment. Consider applying similar principles to efficiency-oriented areas, too.
Adopt agile methods
Utilize agile project management techniques to enhance flexibility and promote rapid adaptability.
- Encourage continuous learning: Foster a culture of ongoing learning and training to keep employees informed about the latest technology trends and market needs. Recognize that learning also means unlearning!
- Adapt error cultures: Ambidexterity explains the error cultures of both worlds. In efficiency areas, a zero error tolerance prevails, and teams and employees are expected to work with meticulous attention to detail. Innovation areas, however, require the courage to make mistakes, to experiment and occasionally step outside with half-baked solutions.
- Allow pilot projects and experiments in innovation areas: Encourage pilot projects and experiments to test innovative ideas in a controlled environment. This allows for making mistakes and learning from them without putting the entire organization at risk.
- Embrace continuous improvement: Establish a process for continuous improvement that encompasses both operational efficiency and innovation. Bear in mind that reviewing and adjusting the strategy on a regular basis is essential.
Conclusion on implementation in banks and insurance companies
Ambidexterity plays a pivotal role for banks and insurance companies in today’s dynamic financial landscape. It empowers them to simultaneously uphold the efficiency of existing business processes while forging new, innovative approaches. Despite the challenges inherent in implementation, long-term competitive advantages can be achieved through targeted measures and a keen focus on key success factors.
A clear vision, top management support, cultural transformation and effective change management are essential to successfully integrate ambidexterity and ensure future-viability.
















































































![Thede Küntzel, Manager Projects & Innovation at Sparkasse Bremen and Managing Director of ÜberseeHub GmbH.]](https://en.bankinghub.comlounge.dev/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/thede-kuentzel-bankinghub-768x549.jpg)